
The value was found to be 9.11 × 10 -10 gĪn electron is that fundamental particles which carries 1 unit negative charge and has a mass nearly equal to 1/1837 th of that hydrogen atom. Thomson whose first experiment was to build a cathode ray tube with a. A cathode-ray tube, often called a CRT, is an electronic display device in which a beam of electrons can be focused on a phosphorescent viewing screen and. Millikan in 1917 with the help of his Oil Drop experiment. A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. These rays were called Cathode Rays and were defined later as electrons. The charge on the electron was found by R.A.

The value was found to be 1.76 × 10 8 coulombs/ gįor the determination of the charge on the electron
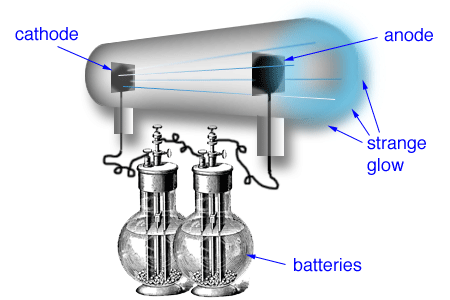
Thomson, led to the discovery of the negatively charged part of the atom, the electron. He found every time that the ratio of charge/mass of the electron was the same. The cathode ray tube experiment, originally carried out by J.J. He used different discharge tubes fitted with electrodes of different metals. How is the flow of current in a cathode ray experiment explained knowing that gases are bad conductors of electricity The gas in the discharge tube experiment. If a laboratory has only CRO in it, other measuring instruments may not be required. The negatively charged material particles constituting the cathode rays are called electrons.įor determination of the ratio of charge/mass of electrons The cathode ray oscilloscope is a versatile laboratory instrument. This indicates that cathode ray produce heating effect.ĥ)They produce green fluorescence on the glass walls of the discharge tube as well as on certain other fluorescent substances such as zinc sulphide.Ħ)They possess penetrating effect ie they can easily pass through thin foils of metals. This shows that cathode rays carry negative charge.Ĥ)When cathode rays strike a metal foil, the latter becomes hot. 3)When an electric field is applied on the cathode rays, they are deflected towards the positive plate of the electric field. Cathode rays, also known as electron beams, are streams of electrons detected in discharge tubes (vacuum tubes).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
